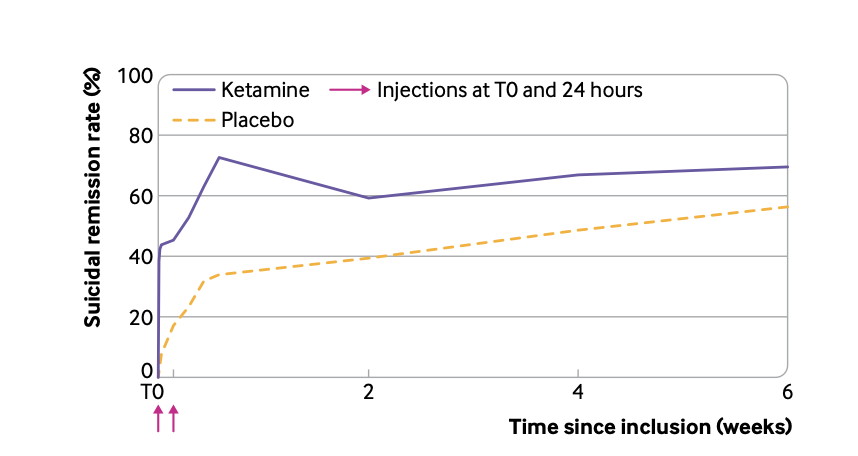
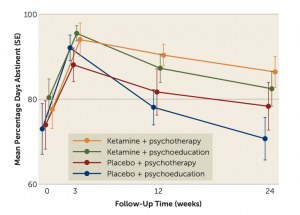
Is Ketamine a Psychedelic? Does it Matter?
 Over the past few years, psychedelics such as LSD and psilocybin mushrooms have garnered much attention as researchers explore their potential use in treating mental health conditions.
Over the past few years, psychedelics such as LSD and psilocybin mushrooms have garnered much attention as researchers explore their potential use in treating mental health conditions.
Ketamine and its close cousin Spravato (esketamine) are often included in this motley crew of psychedelics due in part to their “mind-altering” effects.
Though many are eager to label ketamine a psychedelic, others are less certain, feeling it would be most appropriate to avoid associating ketamine with psychedelics. Let’s explore these different viewpoints to get a clearer sense of whether ketamine is genuinely a psychedelic and why the label matters if it does at all.
What is a Psychedelic?
One obvious way of determining whether ketamine is a psychedelic is by comparing its features to those listed in its definition. Unfortunately, there are no agreed-upon criteria for what makes something a psychedelic drug. Experts waver on the importance of three conditions.
#1: Psychedelics Cause Altered States of Consciousness
 Though there is much disagreement about what counts as a psychedelic, it’s generally accepted that they must induce specific mind-altering effects. Some argue this is all that is required. In other words, they claim that as long as the substance causes a “psychedelic experience,” then it’s a psychedelic.
Though there is much disagreement about what counts as a psychedelic, it’s generally accepted that they must induce specific mind-altering effects. Some argue this is all that is required. In other words, they claim that as long as the substance causes a “psychedelic experience,” then it’s a psychedelic.
But what are psychedelic experiences? While the list is potentially endless, psychedelic experiences are generally thought to impact one’s perception of themselves and the world around them, alter the way they think and reason, and provide insights into how their mind works and the nature of reality. They include experiences like the sense of being at one with the world, distortions of space and time, profound inner peace, ego dissolution, and many more.
#2: Their Conscious Effects Must Have Therapeutic Benefits
While many agree that psychedelics must cause certain altered states of consciousness, some argue that this isn’t enough. They claim that these changes in thought and perception must have a therapeutic effect on the mind or promote psychological growth. As Dr. Yehuda, director of the Center for Psychedelic Psychotherapy and Trauma Research at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York, notes when discussing ketamine’s status as a psychedelic:
The unanswered question in all of this is whether the transpersonal state is what heals you or whether it’s something about the molecule. […] The dissociation or psychoactive effects of ketamine might be incidental. They occur. But that’s not necessarily why the healing is happening.
For these experts, if ketamine’s mind-altering effects have nothing to do with its mental health benefits, then it’s not a psychedelic.
#3: Psychedelics Must Act on Specific Areas in the Brain
In the world of psychedelics, some have been around for longer than others and are more well-studied. For example, mescaline and psilocybin mushrooms have been used since ancient times and were researched heavily in the 1950s and ‘60s. These compounds all appear to affect serotonin (a chemical messenger in the brain) at the “2A” receptor.
Some researchers feel these “classical psychedelics” are the only true ones and that what really matters when deciding whether to categorize a new agent as a psychedelic is how it works in the brain. As Dr. Yehuda notes:
When we talk about chemistry and drug development, we should mostly be defining a psychedelic drug on the basis of the chemistry of the molecule, its pharmacokinetics, and its mechanism of action.
Does Ketamine Meet These Conditions?
How does ketamine stack up against these criteria? As far as its effects on the brain go, ketamine does not act as the classical psychedelics do. It works on N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors, causing an increase of glutamate and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) instead of serotonin. Under this condition, then, ketamine is not a psychedelic.
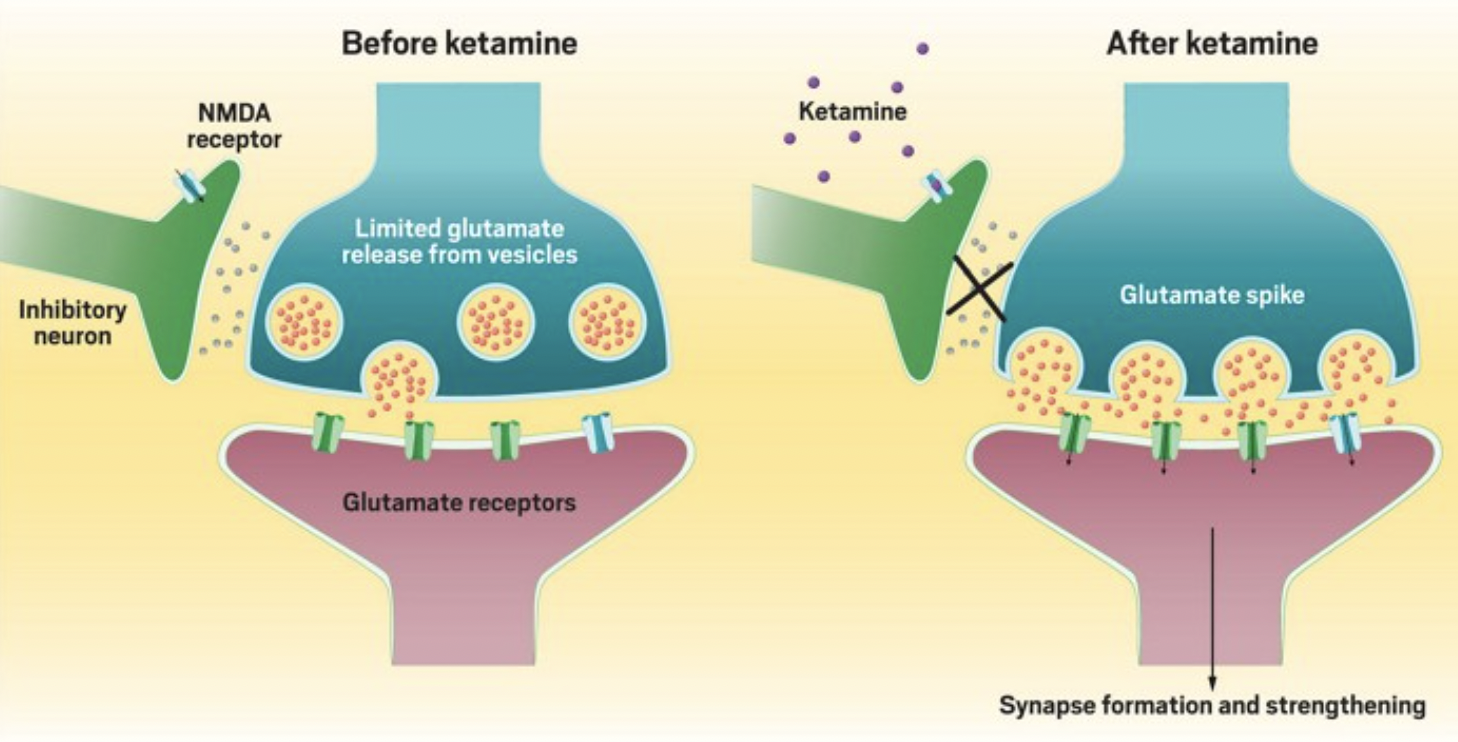
However, acting on a specific set of serotonin receptors is not the only way to produce psychedelic experiences. As Dr. Steve Levine, co-founder of Heading Health, states:
It does appear that subjective psychedelic effects may be induced by a number of stimuli or conditions that also include sensory deprivation, virtual reality, meditation, and suggestibility, among others, and not necessarily mediated through a particular brain receptor.
Importantly, many of these psychedelic experiences can be produced by ketamine. It is most commonly associated with dissociative experiences (i.e., the sense that one is separate from their thoughts and body). It can also cause distortions in one’s perception of space and time. Patients have also reported gaining new perspectives and an enhanced ability to make sense of their thoughts. Rarely, ketamine can cause delusions and delirium, otherwise known as psychotomimetic effects. In many ways, then, ketamine seems to have the right sorts of effects on the mind to be considered a psychedelic.
However, it’s worth highlighting that the experiences won’t be identical to “classical psychedelics.” For example, psilocybin appears more likely to cause what’s known as ego dissolution, where one loses their subjective sense of self. Classical psychedelics may also have a greater tendency to induce visual distortions. In general, because they have different effects on the brain, their conscious effects will differ. As Dr. Arif Noorbaksh, Psychiatrist at Heading, states:
Ketamine is distinct because it works on a completely different neurotransmitter system (glutamate), exerts an effect in different areas of the brain, and as a result, the perceived effects are different. They both result in non-ordinary states of consciousness, but the experience a particular person has when exposed to conventional psychedelics versus ketamine will be different.
When it comes to the therapeutic effects of the altered states of mind that ketamine puts subjects in, the evidence is mixed. A 2020 review concluded that overall, the evidence does not suggest that ketamine’s dissociative effects are responsible for its antidepressant properties. Others argue that ketamine’s ability to cause a shift in perspective and increase cognitive flexibility and open-mindedness are directly responsible for its therapeutic effects. For example, Celia Morgan, professor of psychopharmacology at the University of Exeter, found in a recent experiment that individuals who underwent ketamine and talk therapy experienced longer-lasting antidepressant effects. Professor Morgan notes that talk therapy “requires that individuals think differently about things and learn new ways of thinking about old problems.” As a result, ketamine’s ability to induce shifts in perspective and open-mindedness may explain why it appears to enhance the effects of therapy alone.
Where does this leave us? According to some criteria, ketamine seems to be a psychedelic, while on others, it does not. The answer as to whether ketamine is a psychedelic, then, depends on who you ask and which criteria they feel are most essential.
Does it Matter What We Call It?
Some might think this is all just semantics and that there’s no real principle we can use to determine what to call ketamine.
While the dispute may be verbal, how we talk about ketamine matters. As Dr. Noorbaksh notes:
I think it matters insofar as the term “psychedelic” comes with preconceived notions for many people, and it also places the emphasis on the acute effects of the agent rather than the potentially longer-term effects these agents can have on neuroplasticity, relation to self and others, and other important contributors to mental health.
As a result, it’s important to be mindful of the language we use to describe and categorize ketamine and to avoid clinging to one label or another without regard for how this impacts patients. As Dr. Levine suggests:
Ultimately, whether a molecule is “truly” a psychedelic is likely beside the point. […] Let’s not let feeling precious about terminology distract from the real goal, which is improving well-being in a safe and responsible way.
Talk with your doctor to determine whether this treatment is right for you, or you can schedule an appointment with someone from our team of psychiatrists or therapists to advise you on this or any other potential treatments for depression, including ketamine, Spravato, and TMS. Call us at 805-204-2502 or request an appointment here.
Want to find out if Heading is right for you?
Complete our consultation form and an intake specialist will get in touch.



 What are They Made Of?
What are They Made Of?