Treatment-Resistant Depression
 When treating depression, physicians often prescribe a first-line anti-depressant (e.g., Zoloft, Prozac, and Lexapro). While these treatments work for many, a significant portion find that their symptoms remain even after trying several antidepressants. Known as treatment-resistant depression (TRD), this condition affects around 30 percent of adults with major depressive disorder (MDD).
When treating depression, physicians often prescribe a first-line anti-depressant (e.g., Zoloft, Prozac, and Lexapro). While these treatments work for many, a significant portion find that their symptoms remain even after trying several antidepressants. Known as treatment-resistant depression (TRD), this condition affects around 30 percent of adults with major depressive disorder (MDD).
Despite its prevalence, many are unaware of treatment-resistant depression, how to determine if they might have it, or what to do about it.
Explore answers to these questions and more below.
When is Depression Treatment Resistant?
Treatment-resistant depression is generally defined as a lack of response to a few adequate trials of antidepressants. However, this leaves several questions open, including:
- What counts as a lack of response?
- What is an adequate trial?
- How many antidepressants must a patient have tried?
It’s important to note that there are no universal answers to these questions. Instead of settling them, try answering the following questions:
- Have your treatments failed to make you feel good?
- Do you still not feel like your old self?
- Have the side effects been difficult to manage?
Answering yes to any of these questions means you’re not getting the help you need, and it’s time to talk to your physician, who can decide the next best course of action.
Risk Factors for Treatment-Resistant Depression
Though researchers are still uncovering all traits that can increase the chances of having or developing TRD, we know several factors are associated with the condition. In particular, depression is more likely to be treatment-resistant:
- If it began at an early age
- The longer one has had depression
- The more frequent or longer lasting one’s depressive episodes are
- When there are ongoing stressors
- If one has other physical or mental health conditions
What to Do About Treatment-Resistant Depression
Treatment-resistant depression is treatable. Below are steps you and your physician can take to alleviate your depressive symptoms that haven’t responded to the first few treatments.
- Confirm your diagnosis: Depression that co-occurs with or is caused by other mental health conditions may require a different treatment protocol. As a result, your physician should confirm your diagnosis if your depression isn’t improving in response to treatment.
- Add on talk therapy: Medications often work best when combined with some form of talk therapy. If you find your depression hasn’t responded adequately to your antidepressants, adding on therapy can give them a boost and help alleviate symptoms.
- Change your medications: Just because a few medicines haven’t worked doesn’t mean none will. Newer anti-depressants (e.g., Spravato and Auvelity) that act on different neurotransmitters than first-line treatments can provide relief even when the standard solutions haven’t worked.
- Try a non-medication-based intervention: While oral antidepressants are the most common medical treatment for depression, other options exist. For example, transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a non-invasive procedure where magnetic pulses are used to modulate activity in parts of the brain associated with mood regulation and is FDA approved for treatment-resistant depression.
How We Treat TRD at Heading Health
At Heading, we offer a comprehensive set of solutions to tackle TRD from every angle and provide rapid and sustained relief. We work hard to ensure that cost is not a barrier to accessing the interventions you need. We work with most insurance plans, from United Healthcare to Medicare to Blue Cross Blue Shield, and can provide coverage for all of our services, including ketamine, Spravato, and TMS, for most patients with TRD. Click here for a complete list of participating providers and to schedule a consultation to see whether our solutions are right for you.
Want to find out if Heading is right for you?
Complete our consultation form and an intake specialist will get in touch.



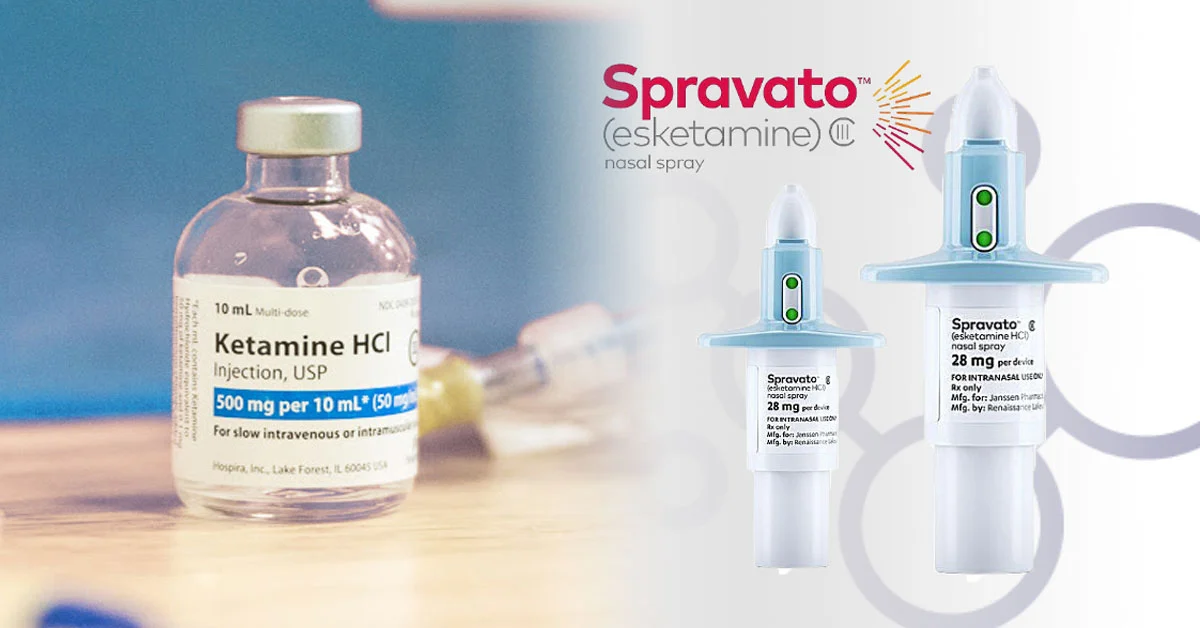
 What are They Made Of?
What are They Made Of?